Business Continuity Planning: Identifying Risks
A business continuity plan is a playbook for continued operations in the event a risk materializes into an incident. Every organization, no matter the domain or environment in which it operates is exposed to risks. Risk identification and management is a critical component of any business continuity plan. For a business continuity plan to be valid, it must address all relevant risks faced by the organization. What is a risk? What is the difference between a risk and a threat? How do you determine the risks for which your organization should prepare?
Risk
A risk can be defined as the product of multiple factors. These factors are:
- Threat
- Probability
- Vulnerability
- Consequence

Threat
The United States Department of Homeland Security (USDHS) defines a threat as “...a natural or man-made occurrence, individual, entity, or action that has or indicates the potential to harm life, information, operations, the environment, and/or property” (p. 14, 2011). A threat is anything that can potentially cause harm, or injury. The operative word here is potential. Therefore, when you think about it, a threat is anything that can possibly have a negative impact on your organization. In other words, anything is possible.
Probability
Probability is the likelihood that a threat will occur. If my favorite team is playing football this weekend, I do not know for certain the outcome. However, based on the analysis of information such as past performance, injuries, location of the game, etc., I can determine the probability of a victory or loss. Based upon the analysis of specific information, an organization can determine the probability of a threat occurring.
Vulnerability
Vulnerability is the level of exposure or susceptibility your organization is to a threat. In hockey, if the score is close and time is running out, the losing team may remove the goalie in an effort to have more offensive players on the ice to increase the chances of scoring. This strategy leaves the losing team’s goal vulnerable. They are susceptible to being scored upon.
Consequence
The consequences come after or as a result of some action. Consequences have a negative connotation. For example, the process used by your organization to produce a product requires the use of hazardous chemicals. By definition, the hazardous chemicals alone pose a threat. Failure to properly use the chemicals may result in a spill. The consequences of the spill may be injury or death to your employees, loss production time, and loss of revenue.
CONCLUSION
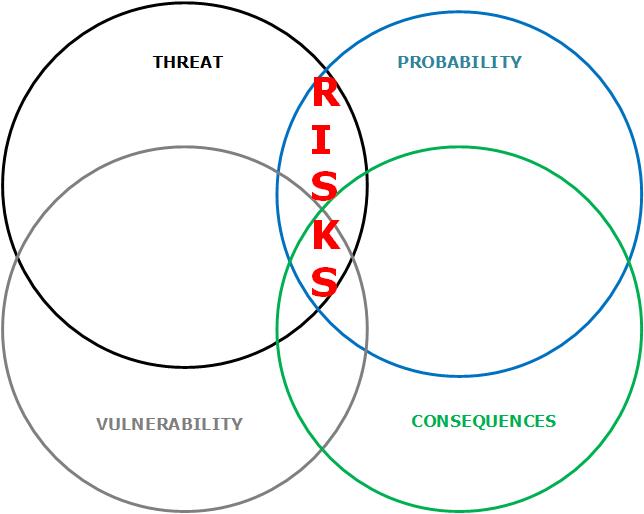
The degree to which these factors overlap is a measure of the level of risks faced by your organization. The rules of math apply in the previously shown formula. If the value of one of the factors is zero, then the product is zero, which means there are no risks.
It requires all of the factors to create a risk. For example, we stated a threat is the possibility of an event occurring. It is possible for a meteor to strike your facility. However, the probability is so small that there is no need to view a meteor strike as a risk.
An organization or community is highly unlikely to eliminate all risks. The best you can hope for is to reduce your risks to an acceptable level. The Nuclear industry uses the acronym ALARA, which stands for As Low As Reasonably Achievable. Reducing the weight of one of the four factors or risks, reduces the chances of a risk occurring or the impact of the risk on your organization if it does occur. Allow R.L. Sligh Limited to assist your organization with managing risks. We can assist your organization and your community with risk identification, risk management, and risk reduction. We are experienced, skilled and capable of helping you protect your organization and community.
"BECAUSE HOPE IS NOT A STRATEGY AND FAILURE IS NOT AN OPTION"
CONTACT US
+724-601-2523
darryl.jones@rlshigh.com
147 Aidan Court
Pittsburgh, PA, 15226
ABOUT
PROGRAMS
JOIN OUR MONTHLY NEWSLETTER
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.



